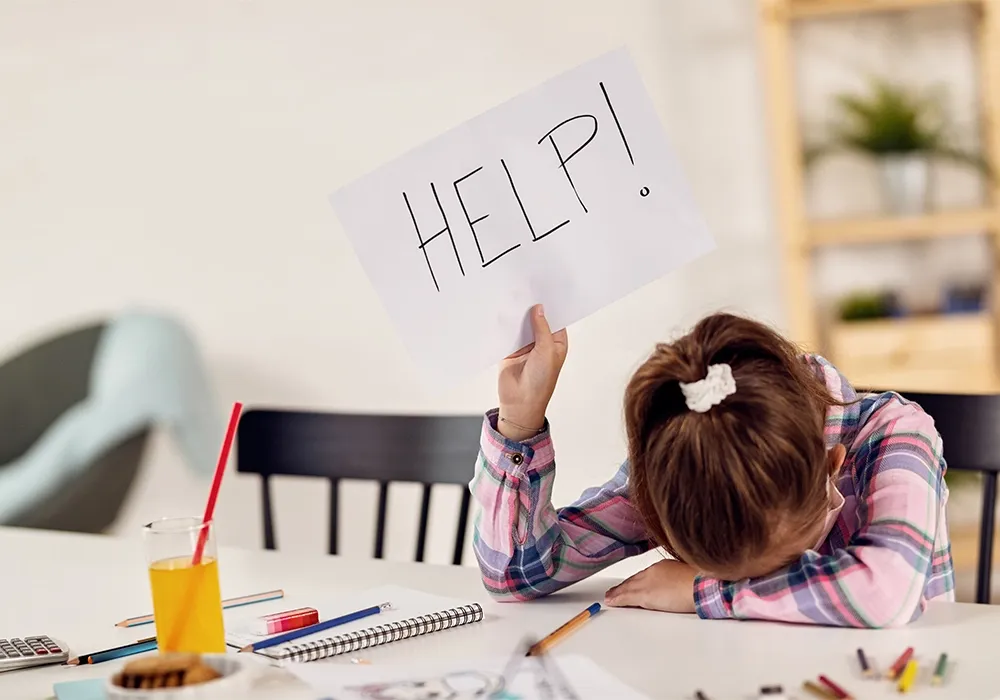

Unattentiveness and hyperactivity in a child are often considered a trait of naughtiness. But what if this situation pertains to their teenage and further continues to adulthood? It is then we realise that what we overlooked as being naughty was ADHD. Hyperactivity and unattentiveness in children and adults can be a sign that they may have ADHD.
Like many other mental health conditions, one gets affected by ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder) from childhood, and this condition goes on to adulthood if left untreated. It is a neurodevelopmental condition where children may have trouble paying attention, control their impulsive behaviours, or are overly active.
Understanding ADHD
As mentioned above, it is normal for kids to be hyperactive and lack focus in their work. But it is a matter of concern if the child does not outgrow these behaviours. If these symptoms persist, it can immensely affect their schooling and college life, and as they grow, it can even start hindering their work life.
Symptoms of ADHD
Attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity (Hyperkinetic disorder) is the most common type. The characteristic clinical features are:
Poor attention span with distractibility
i. Fails to finish the things started.
ii. Shifts from one uncompleted activity to another.
iii. Doesn’t seem to listen.
iv. Easily distracted by external stimuli.
v. Often loses things.
Hyperactivity
i. Fidgety.
ii. Difficulty sitting still in one place for long.
iii. Moving about here and there.
iv. Talks excessively.
v. Interference in other people’s activities.
Impulsivity
i. Acts before thinking on the spur of the moment.
ii. Difficulty in waiting for a turn at work or play.
The symptoms of ADHD in adults include:
- They tend to be careless and have lack of attention to details.
- They prefer and want to do new tasks without completing the old ones.
- They may have poor organising skills.
- They find it difficult to focus and analyse their work.
- They are mostly forgetful and keep on losing their things.
- Most of the time, they are either restless or edgy.
- Finding it difficult to keep quiet and tend to talk out of turn.
- They tend to have constant mood swings, irritability and quick temper.
- They may come out to be impatient.
- Take risks in activities with little or no regard for personal safety and the safety of others.
Impact of ADHD on daily life
The table above shows how the condition of ADHD affects individuals at different stages of life.
Pre-school and Primary school Children
Poor concentration, impulsiveness, and hyperactiveness are some of the common characteristics that you see in these children. They stand out among their classmates for their unusual quietness during recess or for being excessively motor reckless.
When in primary school, the impact of ADHD tends to become more evident in their life as the children realise that they are different from other students in the class. They see that the other kids have developed skills and maturity, making them shine in school, whereas they are still the same. The failures and the rejection they face can lead to low self-esteem.
In cases like this, the school must have an assigned psychologist who can help the child build coping mechanism skills and advise necessary steps that a teacher can take in the classroom.
Teenagers
The condition of ADHD can continue to the adolescent stage, and this can hinder normal health development. The common symptoms or signs of ADHD in teenagers are that they are excessively aggressive or may have developed anti-social behaviour. Reports and studies have also shown that one other reason why teens are having this condition is because of the constant parent-teen conflicts. These anti-social or hyperactive behaviours can directly affect their academics, and you find them getting distracted. Not just in academics, this condition can also directly affect their everyday life, where they may get distracted while driving and suddenly slow down or speed up the vehicle, increasing the risk of accidents.
Adult Life
Research suggests that around 60% of individuals who develop ADHD in childhood continue to experience it into adulthood. Adults who have ADHD have a troubled work-life since they are most likely to be dismissed from employment for their aggressive and hyperactive behaviour. They often try several jobs to see which they are more suitable for, and because of this, they constantly keep moving from one job to another.
Adults with ADHD often have interpersonal conflicts with their colleagues, are often accused of being late or constantly absent, have excessive errors in their work and are unable to meet deadlines of the day.
Studies also show that drug and substance abuse can increase or worsen the condition of ADHD in adults.
Genetic Factors and ADHD
By considering these various factors, we can say that Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD) is a mental health condition influenced by genetic factors as well, and it can affect individuals at different stages of development, during their childhood, adolescence or adulthood.
When it comes to the genetic factors related to ADHD, several genes and genetic variations are identified as potential contributors to the development of the disorder in offspring. The formal heritability of ADHD is about 80% and is higher than most of the other psychiatric conditions. These are some of the prominent genetic factors associated with ADHD.
Dopamine-related genes
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter in the brain that helps to regulate attention and motivation. If there are variations in the genes that encode dopamine receptors, transporters or enzymes, there are high chances of the individual getting affected by ADHD.
Norepinephrine-related genes
Norepinephrine is another neurotransmitter that helps to regulate attention, concentration and impulse control. Any genetic variations in genes related to norepinephrine synthesis, transport and signalling of the ADRA2A gene can signal the chances of ADHD in the individual.
Serotonin-related genes
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation and impulse control, and studies show that there is a potential link between serotonin-related genes HTTLPR and ADHD symptoms related to impulsivity and emotional regulation.
Neurodevelopmental genes
Researchers have conducted many studies to understand the link between the genes involved in brain development and neural connectivity. These studies suggest that SNAP-25 and BDNF genes are involved in synapse formation, neuronal migration and cortical development.
Candidate genes
Although researchers have identified several genes as potential candidates for ADHD susceptibility, more research is needed to establish their role. Studies have shown that genes involved in neurotransmitter regulation and those related to neuronal growth and plasticity contribute to the disorder.
From these, we can conclude that ADHD is a complex disorder contributed by genetic and other factors in its development. It can mean that adults with ADHD are most likely to have children with ADHD, which can contribute to several other problems, and the risk of developing this condition is nine times greater for first-degree relatives
Agan Health is a psychological wellness and mental healthcare centre functioning to help children, adults, women, and the elderly suffering from psychological conditions like anxiety, depression, stress, ADHD and others to break their mental shackles and reinstate them into society.
Counselling
Contact Us
For appointment and consultation:
Bengaluru
BDA complex, 717/1, 16th Main, 6th B Cross Rd, above Child Central Clinic, 3rd Block, Koramangala, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560034
Trichy
#9-A, EVR Road, Aruna Nagar, Puthur, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu 620017
